Technological properties of metallic-diamond tools manufactured by SPS process
Elżbieta Bączek
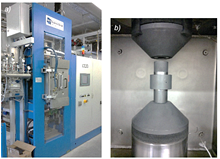
Sintering furnance HP D125 SPS (a), sintering chamber with graphite elements (b)
This paper presents the results of the technological properties of impregnated diamond tools fabricated via spark plasma sintering (SPS) during the process of grinding and cutting of high purity oxides ceramics (ZrO2) stabilized with Y2O3 or MgO. As a metal matrix the water atomized tin bronze and steel-based matrix was used. After sintering, an analysis of microstructure was conducted using scanning electron microscopy. The resulting materials were tested for the apparent density determined by Archimedes’ method, Rockwell hardness (scale B), Young’s modulus, as well as for the technological properties. The performance results of obtained diamond composites were compared with commercial diamond wheel fabricated by HP (hot pressing), usually employed in the grinding of ceramics. Results showed that diamond tools based on Cu-Sn and steel, obtained by SPS, may be successfully used as a matrix in the impregnated diamond tools for cutting or grinding of high-purity oxides ceramics.